# Strapi Content Builder ## Content-types and Fields --- ## What is a Headless CMS? A content management system that: - does not have a front end; - generally exposes data via either a REST API or GraphQL; - can be used with any frontend, such as vanilla JS, ReactJS, Angular and VueJS. --- ### Database Terminology <dl> <dt>Schema (aka: data model)</dt> <dd>The “blueprint” of a database which describes how the data may relate to data.</dd> <dt>Entity (aka: db table)</dt> <dd>A real-world thing or a real-world object.</dd> <dt>Attribute (aka: db table column/field)</dt> <dd>A definition of a characteristic property of an entity.</dd> <dt>Relationship (aka: db join)</dt> <dd>A connection between two entities; either one-to-one, one-to-many or many-to-many.</dd> </dl> --- ## DB terms vs Strapi terms **Schema** --> **Model** **Entity** --> **Content-type** **Attribute** --> **Field** **Relationship** --> **Relation field** --- ## Categories of Strapi Types <dl> <dt>Collection type</dt> <dd>Content-types that can manage several entries.</dd> <dt>Single type</dt> <dd>Content-types that can only manage one entry.</dd> <dt>Components</dt> <dd>A re-usable group of types/fields that can be used in multiple collection types and single types.</dd> </dl> --- ### Regular (boring) content fields Many of the regular types are straight forward: - **Text**: Can be short (i.e. titles) or long (i.e. descriptions) - **Rich Text**: for long format markdown content - **Number**: for quantities, price, etc - **Boolean**: for flags and checkboxes - **Email**: for uhm, email addresses - **Password**: an encrypted field - **Enumeration**: for dropdown menus - **Media**: For example, images - **JSON**: For javascript objects See: [Strapi Documentation](https://docs.strapi.io/user-docs/latest/content-types-builder/configuring-fields-content-type.html#regular-fields) --- ### Relation fields Used for connecting one Content-type to another. 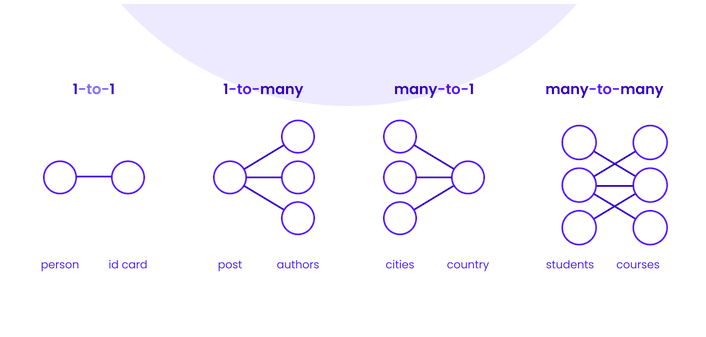 See: [Understanding and using Relations in Strapi](https://strapi.io/blog/understanding-and-using-relations-in-strapi) --- ## One-to-one (rare) Content-type A has and belongs to one Content-type B 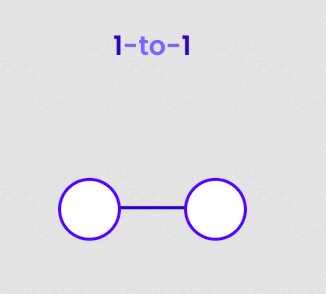 **Example**: A person has a unique ID card. --- ## One-to-many Content-type A belongs to many Content-type B 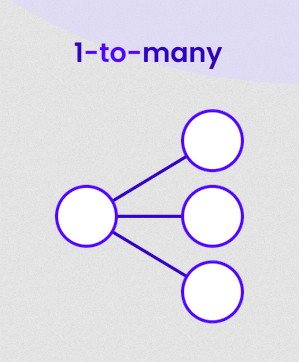 **Example**: A country can have many cities but a city can only be in one country. --- ## Many-to-many Content-type A has and belongs to many Content-type B 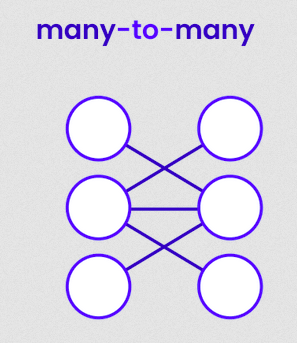 **Example**: A movie can have many actors and an actor can be in many movies. --- ## One way (rare) Content-type A has one Content-type B BUT Content-type B is not linked back to A (uni-directional) Used for performance in large databases. --- ## Many way (rare) Content-type A has many Content-type B BUT Content-type B is not linked back to B (uni-directional). Used for performance in large databases. --- ## Components Used for grouping commonly used sets of fields that are used in multiple Content-types. - Components can be _repeatable_ if a Content-type needs more than one of them. **Example**: a hypertext link is the classic component this groups a link text field with a URL text field. This component can then be used throughout the Content-type Builder. --- ## Further resources - [User Guide](https://docs.strapi.io/user-docs/latest/getting-started/introduction.html) - [Developer Documentation](https://docs.strapi.io/developer-docs/latest/getting-started/introduction.html)