Terminology
- Authentication (tokens)
- The process of ascertaining that somebody really is who they claim to be.
- Authorization (keys)
- Refers to rules that determine who is allowed to do what. E.g. Adam may be authorized to create and delete databases, while Usama is only authorized to read.
Source: Authentication versus Authorization on Stack Overflow
Common types of encryption schemes
API Keys
- Is an authorization scheme that does not authenicate the user.
- Used by developers to access secure APIs.
- An API key is considered public and is inherently insecure.
- The general process for creating a key:
- Login to the service portal.
- Find/generate your API key. This is usually under Settings or similar.
- Copy your API key into your application.
- Follow the instructions provided by the service to test your API key.
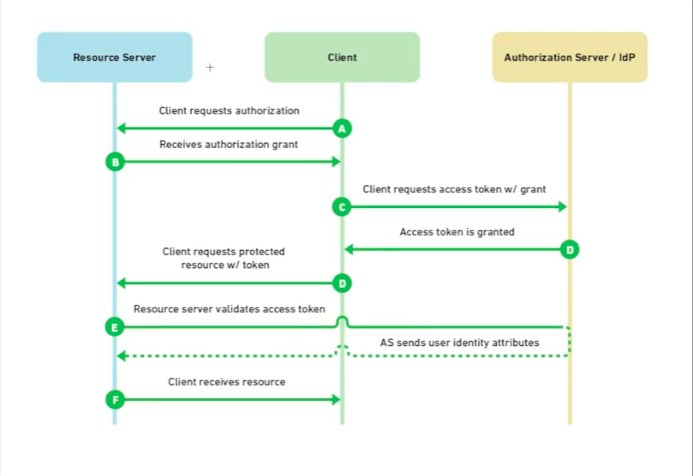
OAuth2
- An authentication standard that grants access to user data using an independent identity provider (IDP).
- Advantages over API keys:
- Access tokens can be tied to particular scopes, which restrict the types of operations and data the application can access
- Combined with refresh tokens, access tokens will expire, so the negative effects could have a limited impact.
- Even if refresh tokens aren’t used, access tokens can still be revoked.
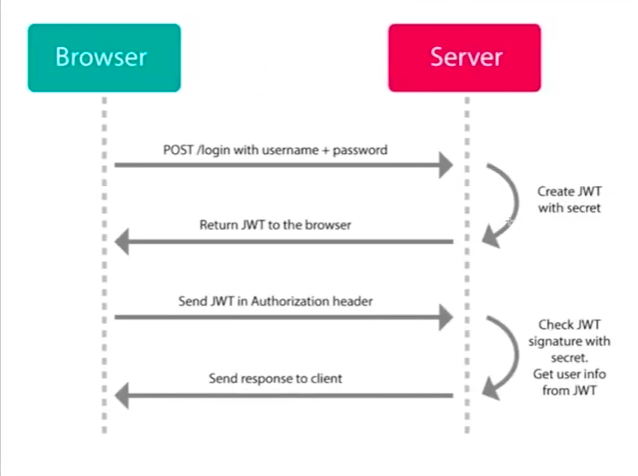
JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
- JWTs can be used for other purposes than API access.
- Is a token scheme that can be used in combination with OAuth.
- Advantage: a JWT can store any type of data, thereby reducing the number of database calls.
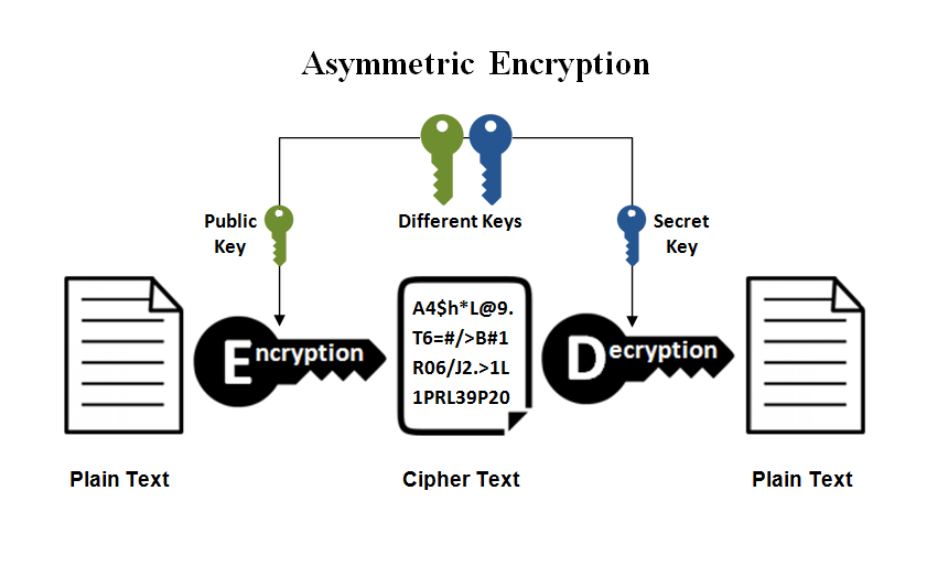
Asymmetric Key Encryption (RSA)
- Also called Public Key Encryption
- 2 keys are needed:
- Public key - known by everyone (generally used for encryption)
- Private key - known only by the owner (generally used for decryption)
- Used a lot for APIs. Keeping the private key hidden and out of repositories is important.
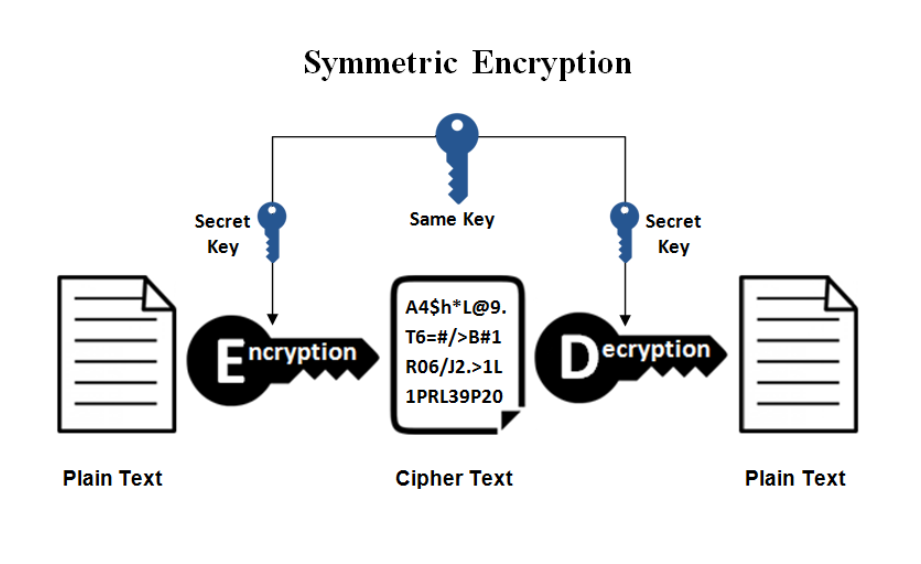
Symmetry Key Encryption
- Also called Secret Key Encryption
- Same key used to encrypt and dycrypt data. The key is blended with the message in a particular way.
- Transer of the key is an issue
- Both the sender and receiver need the same key
- Should be changed frequently to ensure no “leaks”
- Faster than asymmetric encryption
- Best for a limited number of users exchanging information
Attributions
- Why and when to use API keys
- API Keys vs OAuth Tokens vs JSON Web Tokens
-
[OAuth Vs JWT What is the difference?](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a9R3Gq1BKxI)
